1. Knowing Vitamin K

 Studies have underlined more and more the relationship between vitamin K and joint conditions. The synthesis of several proteins linked to bone metabolism and cartilage development depends on this vitamin. More especially, vitamin K stimulates osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium to the bone matrix, therefore boosting bone density and strength. Stable joints depend on healthy bones, which also help to lower the risk of damage and problems associated with joints. Moreover, vitamin K aids in the synthesis of matrix Gla-protein (MGP), so preventing calcification in soft tissues and cartilage and so enhancing general joint condition.
3. How Vitamin K Might Help Osteoarthritis
Studies have underlined more and more the relationship between vitamin K and joint conditions. The synthesis of several proteins linked to bone metabolism and cartilage development depends on this vitamin. More especially, vitamin K stimulates osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium to the bone matrix, therefore boosting bone density and strength. Stable joints depend on healthy bones, which also help to lower the risk of damage and problems associated with joints. Moreover, vitamin K aids in the synthesis of matrix Gla-protein (MGP), so preventing calcification in soft tissues and cartilage and so enhancing general joint condition.
3. How Vitamin K Might Help Osteoarthritis
 Underlying bone and cartilage disintegration define the degenerative joint condition known as osteoarthritis (OA). Studies imply that vitamin K might be preventive in terms of OA development and progression. Reduced symptoms of joint pain and better cartilage conditions have been linked to appropriate amounts of vitamin K. Higher dietary vitamin K consumption has certain studies showing slower OA progression, which emphasizes the need of this vitamin in controlling joint health, especially in older persons.
4. Vitamin K Source Sites
Underlying bone and cartilage disintegration define the degenerative joint condition known as osteoarthritis (OA). Studies imply that vitamin K might be preventive in terms of OA development and progression. Reduced symptoms of joint pain and better cartilage conditions have been linked to appropriate amounts of vitamin K. Higher dietary vitamin K consumption has certain studies showing slower OA progression, which emphasizes the need of this vitamin in controlling joint health, especially in older persons.
4. Vitamin K Source Sites
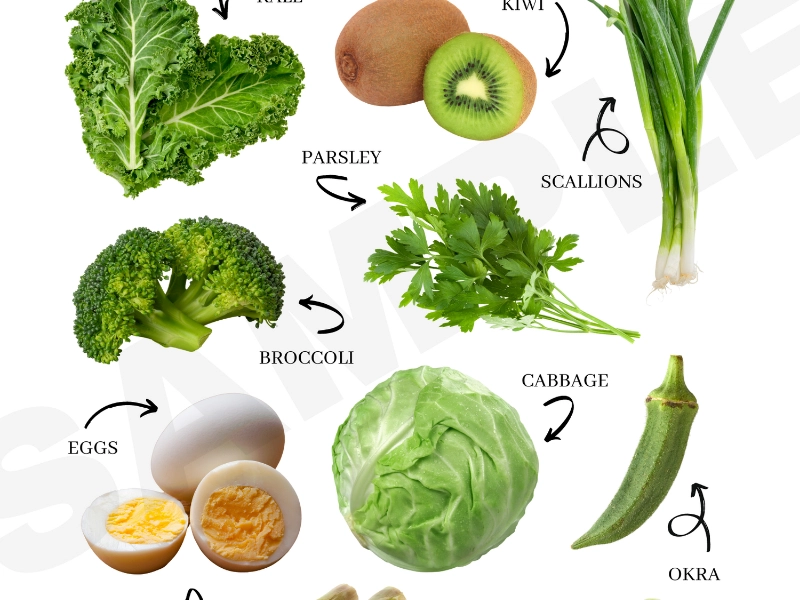
 Including enough amounts of vitamin K in your diet will help you to keep good joints. Great sources of vitamin K1 are leafy green vegetables, including broccoli, kale, and spinach. Rich in vitamin K2 are fermented foods, including natto, a classic Japanese dish created from fermenting soybeans. Other sources consist in meat, eggs, and dairy goods. Although pills might be taken into consideration for individuals who might find it difficult to receive enough vitamin K from food alone, it is important to see a doctor before beginning any kind of supplementation.
5. Value of Calcium and Vitamin D
Including enough amounts of vitamin K in your diet will help you to keep good joints. Great sources of vitamin K1 are leafy green vegetables, including broccoli, kale, and spinach. Rich in vitamin K2 are fermented foods, including natto, a classic Japanese dish created from fermenting soybeans. Other sources consist in meat, eggs, and dairy goods. Although pills might be taken into consideration for individuals who might find it difficult to receive enough vitamin K from food alone, it is important to see a doctor before beginning any kind of supplementation.
5. Value of Calcium and Vitamin D
 Although joint health depends on vitamin K, it complements other nutrients, most especially vitamin D and calcium. Strong bones depend on calcium absorption being enhanced by vitamin D. These elements, taken together, support joint structure and operation. Calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin K taken in balance will help to guarantee ideal joint health and bone density. This symbiotic link highlights the need for a balanced diet that supplies all required elements to preserve good joints.
6. How Aging Affects Joint Health
Although joint health depends on vitamin K, it complements other nutrients, most especially vitamin D and calcium. Strong bones depend on calcium absorption being enhanced by vitamin D. These elements, taken together, support joint structure and operation. Calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin K taken in balance will help to guarantee ideal joint health and bone density. This symbiotic link highlights the need for a balanced diet that supplies all required elements to preserve good joints.
6. How Aging Affects Joint Health
 Often resulting from a mix of elements including decreased physical activity, loss of muscle mass, and changes in bone density, aging raises the likelihood of joint-related problems. Deficiency of vitamin K can aggravate these problems and cause weaker bones and more joint discomfort. Older persons especially need enough vitamin K to sustain joint health and lower their risk of diseases such as osteoarthritis. Part of aging healthily, regular visits to healthcare experts can assist in monitoring vitamin levels and general joint health.
7. Lifestyle Choices Promoted for Joint Integrity
Often resulting from a mix of elements including decreased physical activity, loss of muscle mass, and changes in bone density, aging raises the likelihood of joint-related problems. Deficiency of vitamin K can aggravate these problems and cause weaker bones and more joint discomfort. Older persons especially need enough vitamin K to sustain joint health and lower their risk of diseases such as osteoarthritis. Part of aging healthily, regular visits to healthcare experts can assist in monitoring vitamin levels and general joint health.
7. Lifestyle Choices Promoted for Joint Integrity
 Apart from guaranteeing sufficient intake of vitamin K, other lifestyle choices might help to maintain joint condition. Strength training and flexibility exercises, among other regular physical activities, help preserve joint function and lower stiffness. Maintaining a good weight is also rather important since extra weight strains hips and knees especially. Additionally helping to maintain general joint health is keeping hydrated and avoiding too much alcohol and tobacco usage. People can better support their joints by using a whole strategy including food, exercise, and good behaviors.
8. Review of Vitamin K's Function in Joint Maintenance
Apart from guaranteeing sufficient intake of vitamin K, other lifestyle choices might help to maintain joint condition. Strength training and flexibility exercises, among other regular physical activities, help preserve joint function and lower stiffness. Maintaining a good weight is also rather important since extra weight strains hips and knees especially. Additionally helping to maintain general joint health is keeping hydrated and avoiding too much alcohol and tobacco usage. People can better support their joints by using a whole strategy including food, exercise, and good behaviors.
8. Review of Vitamin K's Function in Joint Maintenance
 All things considered, vitamin K supports bone density, cartilage health, and general joint function, therefore preserving good joints. Its relevance is shown by its participation in the synthesis of proteins necessary for cartilage calcification prevention and bone metabolism. You may help to maintain joint health and maybe lower the risk of joint-related problems by including foods high in vitamin K into your diet and thinking about the combined impact of other nutrients, including vitamin D and calcium. Better quality of life and healthier joints can result from a proactive attitude toward diet and lifestyle.
All things considered, vitamin K supports bone density, cartilage health, and general joint function, therefore preserving good joints. Its relevance is shown by its participation in the synthesis of proteins necessary for cartilage calcification prevention and bone metabolism. You may help to maintain joint health and maybe lower the risk of joint-related problems by including foods high in vitamin K into your diet and thinking about the combined impact of other nutrients, including vitamin D and calcium. Better quality of life and healthier joints can result from a proactive attitude toward diet and lifestyle.